Packaging Education, Plastic Bottles
23 Popular Facts About HDPE Bottles
As our packaging education suite is always growing with new content for curious visitors seeking the answers to their needed questions. We decided to use the top questions from AlsoAsked.com for the search term ‘HDPE bottles’. Users on the internet typing into the Google search bar tend to ask many questions. A search engine will seek pages from websites worldwide that offer up information that is helpful, popular or authoritative. Knowledge can be produced in the form of text, images or video, enabling the material to be presented in many different styles.
With this in mind, our packaging experts have decided to answer 23 questions that dig deeper into the world of HDPE bottles. We can only hope that all your questions about HDPE bottles can be answered in one location (our power article), saving you precious time and energy for product ideas and new innovations.
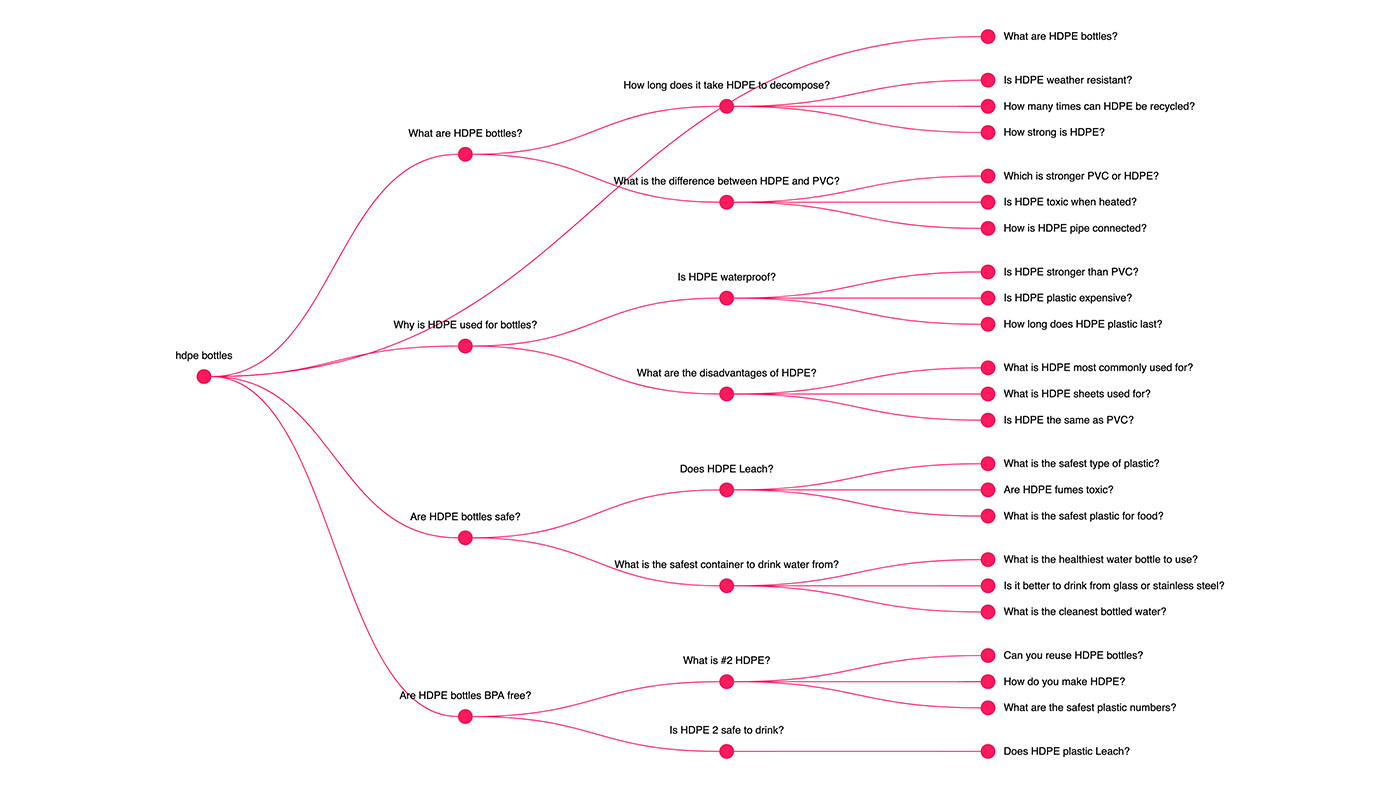
AlsoAsked Results
#1 What Are HDPE Bottles?
HDPE bottles are plastic containers with a huge range of capacities, allowing the storage and dispensing of different liquids. High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) bottles are widely used in the UK for drinking liquids, toiletry, detergents and cosmetic products. Milk is usually stored using HDPE plastic bottles because it’s cheap to manufacture, and the plastic is widely recyclable. HDPE bottles can also be colour coded to help with brand marketing or colour labelling. HDPE bottle lids for fresh milk can be in blue, green or red, helping the consumer pick the correct option.
#2 Why Is HDPE Used For Bottles?
HDPE is used for several reasons, especially for products that offer a liquid, cream, serum or gel solutions. Here are our top 12 reasons:
-
- Cheap to produce and manufacture
- It can be made into almost any design from cad models
- Easy to work with – HDPE bottle can be produced into many different shapes and sizes using blow moulding equipment
- It can be colour coded
- It is renowned for its high strength
- Can withstand high temperatures for short periods
- HDPE can be bacteria-resistant for use in food packaging and life-saving medical equipment
- Works well in most environmental conditions and exceeds crack and stress-resistant testing
- A thin plastic finish that is durable for many industry needs for end consumer needs
- HDPE bottles are a sustainable option because they are fully recyclable, can be integrated back into the recycling chain, and are very lightweight, which is less expensive for transportation and easier on carbon emissions
- HDPE bottles can be used as monolayer bottles for pasteurised milk or as coextruded bottles with barrier layers for UHT or sterilised liquids
- Most HDPE bottles are widely recycled in the UK, figures show that HDPE bottles are recycled around 79% of the time.
#3 Are HDPE Bottles Safe?
HDPE products are safe and are not known to transmit any chemicals into foods or drinks, making this plastic a low health risk to human use. Chemical Safety Facts.org explains: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates the safety of all plastics currently used in food packaging and food contact materials. A list of these approved substances can be found in FDA’s database.
#4 Are HDPE Bottles BPA Free?
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is, like BPA, a material derived from petroleum. The difference is that HDPE plastics are completely free from BPA and are, therefore, safe for applications that directly impact humans.
#5 How Long Does It Take HDPE To Decompose?
The plastic decomposing question is difficult to answer because a few variables need to be considered. Variables include thickness, mass, and the amount of raw material used. If the HDPE bottle is thinner in design and shape, the quicker it will erode in a landfill.
pubs.acs.org have studied plastic decomposing and concluded:
‘The amount of plastics accumulating in the environment is growing rapidly, yet our understanding of its persistence is minimal. This Perspective summarizes the existing literature on environmental degradation rates and pathways for the major types of thermoplastic polymers. A metric to harmonize disparate types of measurements, the specific surface degradation rate (SSDR), is implemented and used to extrapolate half-lives. SSDR values cover an extensive range, with some of the variability arising due to degradation studies conducted in different natural environments. SSDRs for high-density polyethylene (HDPE) in the marine environment range from practically 0 to approximately 11 μm year−1. This approach yields several interesting insights. Using a mean SSDR for HDPE in the marine environment, linear extrapolation leads to estimated half-lives ranging from 58 years (bottles) to 1200 years (pipes). For example, SSDRs for HDPE and polylactic acid (PLA) are surprisingly similar in the marine environment, although PLA degrades approximately 20 times faster than HDPE on land. Our study highlights the need for better experimental studies under well-defined reaction conditions, standardized reporting of rates, and methods to simulate polymer degradation using’.
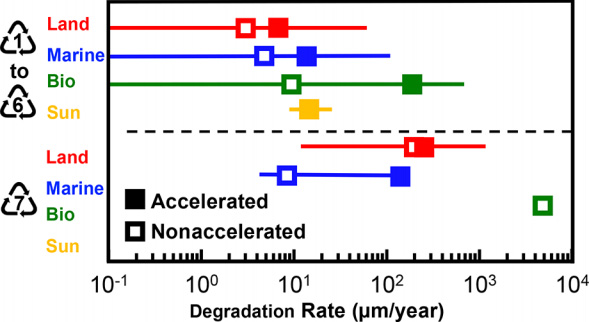
Source from pubs.acs.org
#6 What Is The Difference Between HDPE And PVC?
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a cheap and durable vinyl polymer used in construction projects and some cosmetics. At the same time, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) is a polyethylene thermoplastic that is made from petroleum. PVC is heavier and stronger while HDPE is harder and more abrasion and heat resistant. PVC is also difficult to recycle and has been phased out of 98% of Berlin Packaging UK’s products.
#7 Is HDPE Waterproof?
HDPE is appropriate for waterproofing and storing liquids safe in an HDPE container. The HDPE vessel can be airtight, which helps to keep the product free from bacteria, dirt, dust and other anomalies that you don’t want mixing with the product.
What Are The Disadvantages Of HDPE?
HDPE does, unfortunately, have a few disadvantages for the consumer, manufacturer and brand owners. These include:
- Not Resistant to Oxidizing Acids
- Not Resistant to Chlorinated Hydrocarbons
- Not Biodegradable
- Poor Weathering
- Highly Flammable
- Sensitive to Stress Cracking
- Can’t Be Composted
- High Thermal Expansion
- Poor Temperature Capability
#8 Does HDPE Leach?
Some HDPE compositions have been shown to leach minimal amounts of estrogenic chemicals (chemicals having estrogenic activity – (EA) ) through different liquid types. Further studies have been commissioned to see if this EA activity is having harmful effects on human health (cell formation or deterioration). For further reading on this subject, we recommend this report from ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
#9 What Is The Safest Container To Drink Water From?
Glass is the safest water bottle type because it’s chemical-free, made from natural materials, and dishwasher-safe.
#10 What Is #2 HDPE?
High-density Polyethylene or HDPE is a very durable and robust plastic, which is why it’s so widely used. You can identify it by the plastic number #2 symbol, a two inside the chasing arrows.

High-density Polyethylene is a thermoplastic and is made up of ethylene monomers. Once these are formed into polymers, they line up in a regular pattern making it dense in structure and, therefore, a solid material.
HDPE can be found in both rigid and soft items. Some common uses of Plastic number 2 are:
- Milk bottles
- Water bottles
- Juice bottles
- Shampoo Bottles
- Soap containers and tubes
- Conditioner bottles
- Face and body personnel care products
- Household cleaners and detergents.
#11 Is HDPE Weather Resistant?
HDPE products resist
all weather conditions and deflect other problems, including rotting, insects, mildew and mould. Because HDPE has such high impact, chemical, and weather resistance, HDPE can outlast traditional materials while being lightweight and versatile. HDPE does not shatter, tear, snap or break if you drop it, although HDPE bottles or containers can be punctured with a sharp object. These factors are what give HDPE popularity in the domestic and commercial market sectors.
#12 How Many Times Can HDPE Be Recycled?
Scientists prove HDPE can be recycled at least 10 times.
#13 How Strong Is HDPE?
HDPE is known for its high strength-to-density ratio. The density of HDPE can range from 930 to 970 kg/m3. Although the density of HDPE is only marginally higher than that of low-density polyethylene, HDPE has little branching, giving it stronger intermolecular forces and tensile strength than LDPE. The difference in strength exceeds the difference in density, giving HDPE a higher specific strength. It is also harder and more opaque and can withstand somewhat higher temperatures (120 °C/248 °F for short periods). High-density polyethylene, unlike polypropylene, cannot withstand normally required autoclaving conditions. The lack of branching is ensured by an appropriate choice of catalyst and reaction conditions. Source
#14 Which Is Stronger PVC Or HDPE?
Both are strong and durable, but their strengths vary and they have different applications. PVC is heavier and stronger while HDPE is harder and more abrasion and heat resistant.
#15 Is HDPE Toxic When Heated?
Some plastics are toxic to the health of humans while in the manufacturing process. The correct precautions need to be taken seriously, and any fumes need to be disposed of carefully. The dust or resin of polyethylene, for example, can cause eye irritation as can the vapours from the resin when it’s being heated. It is also important not to burn any plastic after use, and use the correct recycling facilities supplied on your premises. If you lack the correct disposing bins, you should be able to source a local recycling centre that can help you with any disposal needs.
However, HDPE creates no harmful emissions in the production process, and during its consumption cycle, it has become the most preferred kind of thermoplastic. It leaks no toxic waste in soil or water, which makes it more environmentally friendly. Recently it is seen that there is a large shift in demand for this polymer than other polymers.
#16 Is HDPE Plastic Expensive?
HDPE plastic is made by applying immense heat to petroleum under controlled conditions. This process is known as “cracking”, which helps to create ethane gas. In this process, gas molecules attach together to form polymers, which are further used to produce polyethylene.
After this process, moulding of polyethylene is done to produce a stronger polymer material known as high-density polyethylene, applicable to a variety of uses and applications. HDPE requires heat which can be relatively cheap to produce and manufacture. Trend reports show that it HDPE consumption is growing year on year.
Polyethylene is one of the most used polymer globally. The production of polyethylene polymer globally was 103 million tons in 2016. The production of high-density polyethylene on was 47.5 million tons in 2016. It occupied a share of 46% of total polyethylene production globally.
#17 What Is HDPE Most Commonly Used For?
HDPE is commonly used in food packaging for juice and milk jugs, squeeze butter and vinegar bottles and chocolate syrup containers, as well as grocery bags. Berlin Packaging UK tends to use HDPE in a number of cosmetic products, including:
#18 Is HDPE The Same As PVC?
HDPE and PVC look similar but are used for a range of different products and are made slightly differently. First, let’s compare their properties.
HDPE
| Chemical Formula | (C2H4)n |
| Density | 940 kg/m3 |
| Melting Point | 130.8 °C. |
PVC
| Chemical Formula | (C2H3Cl)n |
| Density | 1.3–1.45 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 100 °C (212 °F) to 260 °C (500 °F) |
As you can see from the table data PVC and HDPE plastic are made up of different properties. Both end products have disadvantages and advantages for commercial or domestic use. Let’s look at HDPE and PVC through a comparison of Pros and cons.

| PROS | CONS |
| Low cost & high stiffness | Difficult to melt process |
| Intrinsic flame retardant | Limited solvent stress cracking resistance |
| FDA compliant & also suitable for transparent applications | Becomes brittle at 5°C (when not modified with impact modifiers and/or processing aids) |
| Better chemical resistance than plasticized PVC | Low continuous service temperature of 50°C |
| Good electrical insulation & vapor barrier properties | – |
| Good dimensional stability at room temperature | – |
| PROS | CONS |
| Low temperature impact resistance | Poor Weathering |
| Excellent chemical resistance – resistance to corrosion, tuberculation, deposits | Highly Flammable |
| Safety of potable water and long-term reliability | Sensitive to Stress Cracking |
| Freeze-break resistance | Not Biodegradable – Can’t Be Composted |
| Recyclable, eco-friendly material | Not Resistant to Oxidizing Acids |
| Heat fusible for virtually leak-free performance | Not Resistant to Chlorinated Hydrocarbons |
| Lightweight, easy to transport | High Thermal Expansion |
#19 What Is The Safest Type Of Plastic?
Plastic packaging containers are given resin codes which can be found on the bottom of the container or inserted on the label. This makes it easy for the consumer to see what they buying before making a decision to purchase.
These resin codes are considered safer: #2 HDPE, #4 LDPE, and #5 PP.
#2 HDPE (high-density polyethylene) include: bottled milk, water and juice and yoghurt cups.
#4 LDPE (low-density polyethylene): bags for bread, frozen foods and fresh produce, PVC-free consumer cling wraps, re-sealable zipper bags and some bottles.
#5 PP (polypropylene): food storage containers, deli soup, yoghurt containers, straws and other clouded plastic containers, including baby bottles.

#20 What Is The Safest Plastic For Food?
HDPE, LDPE and PP are the safest plastics for food or drinking containers.
#21 Is It Better To Drink From Glass Or Stainless Steel?
Glass is the safest water container type and offers purity of taste, but stainless steel offers insulation benefits that keep your beverages hot or cold.
#22 Can You Reuse HDPE Bottles?
HDPE bottles can be recycled up to ten times or reused by the consumer for a period of time. HDPE plastic bottles should be washed between uses, so they don’t contain bacteria. Use warm (not hot) soapy water. Rinse thoroughly before refilling. We don’t recommend putting soft plastic bottles in the dishwasher as this could change the shape of the container or, in some cases, cause leaching in different plastic types.
It’s important to note that it’s not been definitively proven that nonylphenol can leach out of HDPE bottles. High-density polyethelene is sturdy and designed to ward off bacterial growth. Manufacturers tend to use HDPE for a different range of bottle sizes, but these bottles are intended for only one-time use. This is why they have become widely recyclable.
#23 How Do You Make HDPE?
See question 16.
Did we answer all of your questions about HDPE bottles? Did we miss something that needs answering? If so, please leave our team a comment below, and we promise to get back to you.



